Research Symposium
25th annual Undergraduate Research Symposium, April 1, 2025
Charu Gopal Poster Session 2: 10:45 am - 11:45 am/ Poster #77
BIO
Hi, my name is Charu Gopal. I am a senior at Florida State University pursuing a B.S. in Economics with minors in Statistics and Business. My experience in finance and energy markets through past internships shaped my analytical skills, but my genuine interest lies in behavioral economics and econometrics. In fall 2024, I joined the DeVoe L. Moore Center as a public policy intern to deepen my understanding of economic research and policy analysis. Looking ahead, I aim to expand my research experience in graduate school, focusing on data-driven insights to address complex economic challenges.
Quantitative Research Techniques For New Policy Researchers: Examples from Housing and Crime Literature
Authors: Charu Gopal , Crystal TaylorStudent Major: Economics
Mentor: Crystal Taylor
Mentor's Department: Urban & Regional Planning department Mentor's College: College of Social Sciences and Public Policy Co-Presenters:
Abstract
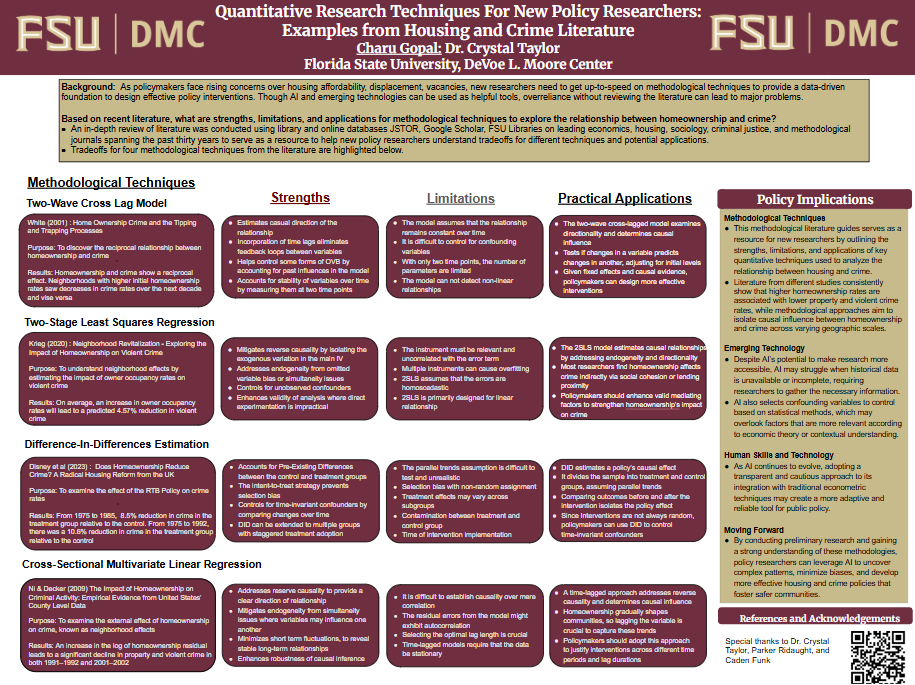
Homeownership is widely associated with lower crime rates compared to renting, as homeowner-dominated communities tend to foster stronger social ties and crime prevention. However, the homeownership-crime relationship is not always straightforward even for researchers. Factors such as transient populations (e.g., college students), different geographical locations, neighborhood resources, socio-economic dynamics, and the local policy landscape can disrupt neighborhood effects. Based on recent literature, what are the methodological best practices to explore the relationship between homeownership and crime? An in-depth review of literature was conducted using library and online databases JSTOR, Google Scholar, FSU Libraries on leading economics, housing, sociology, criminal justice, and methodological journals spanning the past thirty years. The research used the following search terms homeownership, crime, neighborhood, relationship, empirical analysis for this review. For highly cited papers, reference lists were reviewed. Preliminary results reveal four main methodological techniques used for housing and crime research: (A) a cross-sectional multivariate linear regression to help address reverse causality, where crime may deter homeownership decisions; (B) a two-stage least squares regression to isolate exogenous variation in homeownership through an instrument; (C) a difference-in-differences estimation to compare policy impact under the parallel trends assumption; and (D) a two-wave cross-lag model to analyze the reciprocal relationship between homeownership and crime. These methodologies contribute to ongoing debates on the role of homeownership in crime prevention and offer practical insights for future researchers.
Keywords: Homeownership, Crime, Relationship, Empirical Analysis