Research Symposium
25th annual Undergraduate Research Symposium, April 1, 2025
Paulos Samuel Poster Session 4: 3:00 pm - 4:00 pm/ Poster #217

BIO
I'm Paulos, originally from Orlando, and have a strong passion for science, medicine, and global health. I’m currently involved in research on fatty liver disease, studying how a certain protein, YBX1, can affect gene expression and play a role in obese patients. It’s been exciting to explore how molecular mechanisms can shape health outcomes and potential treatments.
Outside of academics, I’m part of the Phi Delta Epsilon medical fraternity, and stay active on campus through the African Student Association and my Intramural basketball team. I’m also an Eagle Scout, and have a love for the outdoors—hiking and exploring nature is still one of my favorite ways to recharge.
In the future, I plan to become a physician and hope to combine clinical work with research and service. I’m still deciding between ophthalmology and gastroenterology, but I know I want to contribute meaningfully to healthcare, both in private practice and in underserved communities around the world. My goal is to help bridge gaps in access and bring innovation and compassion to every part of my medical journey.
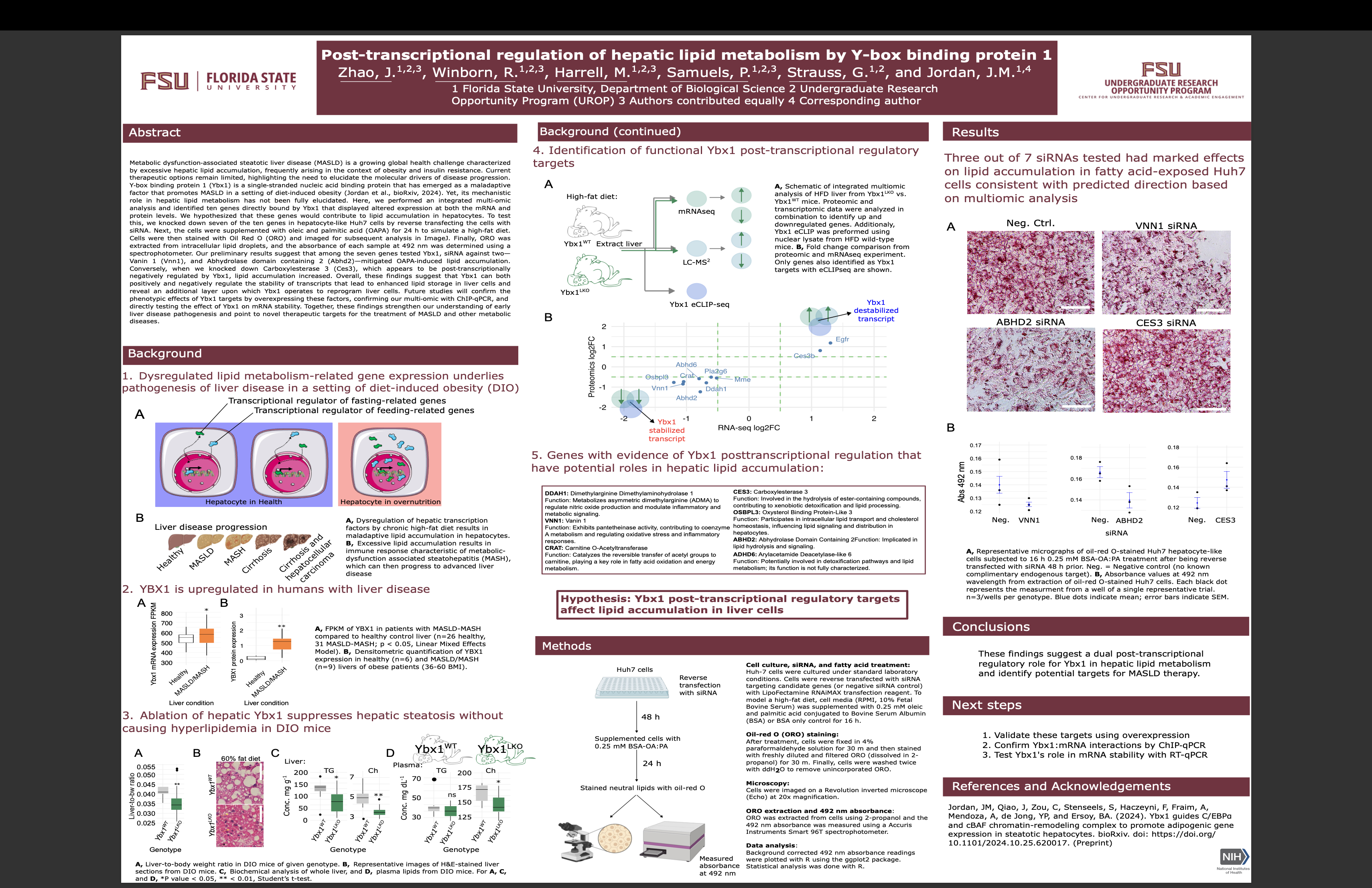
Post-transcriptional regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by Y-box binding protein 1
Authors: Paulos Samuel, Dr. James JordanStudent Major: Cell & Molecular Neuroscience
Mentor: Dr. James Jordan
Mentor's Department: Biological Science Mentor's College: Florida State University Co-Presenters:
Abstract
Metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a growing global health challenge characterized by excessive hepatic lipid accumulation in the setting of obesity and insulin resistance. Current therapies remain limited, underscoring the need to identify molecular drivers of disease progression. Y‐box binding protein-1 (Ybx1) is a single‐stranded nucleic acid binding protein implicated in MASLD in diet‐induced obesity (Jordan et al., bioRxiv, 2024), yet its role in hepatic lipid metabolism remains unclear. We performed an integrated multi‐omic analysis and identified ten genes bound by Ybx1 that displayed altered mRNA and protein expression. We hypothesized that these genes contribute to lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. To test this, we knocked down eight of these genes in hepatocyte‐like Huh7 cells using siRNA. Cells were then exposed to 0.25 mM oleic and palmitic acid for 16 hours to mimic a high‐fat diet, stained with Oil Red O, and analyzed using ImageJ. Lipid content was quantified by extracting Oil Red O from intracellular droplets and measuring absorbance at 492 nm. Preliminary results indicate that among seven genes with transcripts stabilized by Ybx1, siRNA against three—Carnitine O-Acetyltransferase (CRAT), Vanin 1 (Vnn1), and Abhydrolase domain containing 2 (Abhd2)—reduced lipid accumulation. In contrast, knockdown of Carboxylesterase 3 (Ces3), a gene negatively regulated by Ybx1, increased lipid storage. These findings reveal a dual regulatory role for Ybx1 in hepatic lipid metabolism and identify potential targets for MASLD therapy. Future work will validate these targets using overexpression, confirm Ybx1:mRNA interactions by ChIP‐qPCR, and test Ybx1’s role in mRNA stability with RT-qPCR.
Keywords: MASLD, Liver, Obesity, Epigenetics, RNA