Research Symposium
25th annual Undergraduate Research Symposium, April 1, 2025
Alexander Campbell Poster Session 2: 10:45 am - 11:45 am/ Poster #36

BIO
Prudential second year pre-med student with an interest in learning and applying innovative, clinical, and methodological techniques to derive solutions. I am dynamic and collaborative in providing quality results in the disciplines of research and medicine
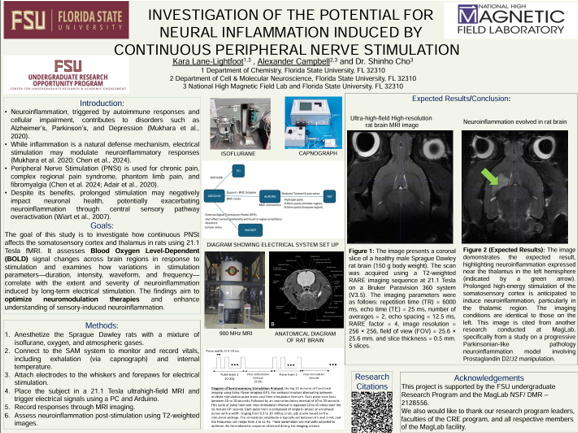
INVESTIGATION OF THE POTENTIAL FOR NEURAL INFLAMMATION INDUCED BY CONTINUOUS PERIPHERAL NERVE STIMULATION
Authors: Alexander Campbell, Dr. Shinho ChoStudent Major: Cell and Molecular Neuroscience
Mentor: Dr. Shinho Cho
Mentor's Department: National High Magnetic Lab Mentor's College: Florida State University Co-Presenters: Kara Lane-Lightfoot
Abstract
Peripheral nerve stimulation is used for chronic pain management, rehabilitation, and studying nerve responses and regeneration mechanisms. However, continuous high-frequency stimulation can overactivate the brain's somatosensory areas, potentially inducing or worsening neural inflammation. Despite its widespread use, the effects of stimulation intensity, frequency, duration, and current characteristics on neural networks like the somatosensory cortex and thalamus are not well understood.
This study aims to investigate how electrical stimulation of the rat's whisker area and forepaw affects the somatosensory cortex and thalamus. Utilizing high-speed, high-resolution functional MRI at 21.1 Tesla, we will explore how different stimulation parameters influence neural activity and the potential for inflammation. Specifically, we'll examine functional and structural changes in sensory processing networks.
We hypothesize that such stimulation activates neuroinflammatory mechanism, detectable through changes in T2-weighted images and molecular markers of inflammation. Anticipated results may show that peripheral electrical stimulation contributes to inflammation in targeted cortical regions. This study could provide insights into the mechanisms linking sensory stimulation to neuroinflammatory processes and aid in modeling or evaluating treatments for neurological conditions like neural inflammation, nerve damage, and nerve regeneration.
Keywords: Neural Inflammation