Research Symposium
24th annual Undergraduate Research Symposium, April 3, 2024
Jordan Cheze Poster Session 3: 1:30 pm - 2:30 pm /201

BIO
Jordan Cheze is an undergraduate Meteorology student from Brooksville, Florida. She is involved with the American Meteorological Society and National Weather Association of North Florida and the Students for the Exploration and Development of Space at FAMU-FSU, where she serves as the Project Director. Outside of school, Jordan is an intern with the Bureau of Land Management out of Idaho Falls.
Simulating and Analyzing Wildland Fire Spread
Authors: Jordan Cheze, Bryan QuaifeStudent Major: Meteorology
Mentor: Bryan Quaife
Mentor's Department: Scientific Computing Mentor's College: Arts and Sciences Co-Presenters:
Abstract
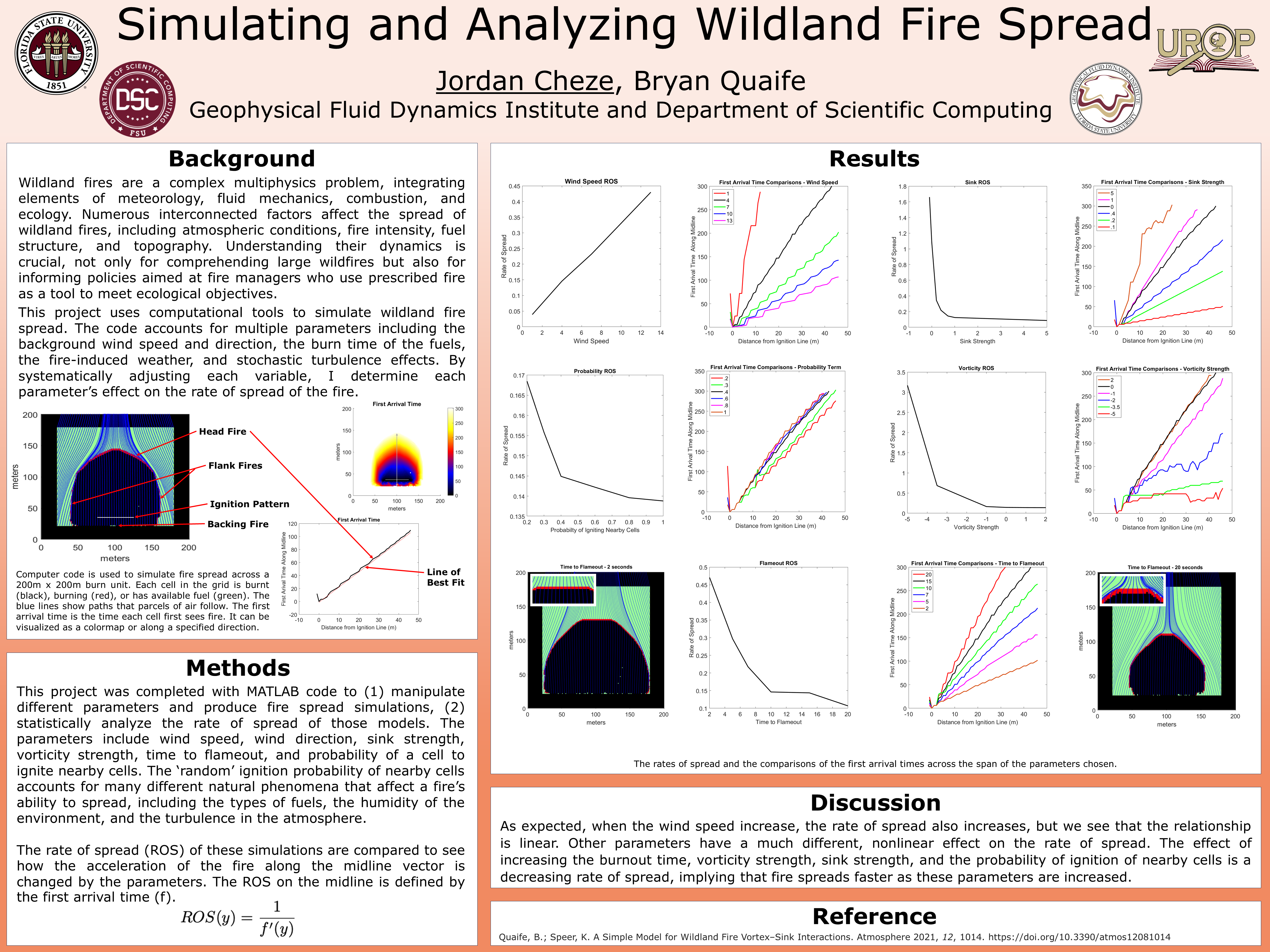
Wildland fires are a complex multiphysics problem, integrating elements of meteorology, fluid mechanics, combustion, and ecology. Numerous interconnected factors affect the spread of wildland fires, including atmospheric conditions, fire intensity, fuel structure, and topography. Understanding their dynamics is crucial, not only for comprehending large wildfires but also for informing policies aimed at fire managers who use prescribed fire as a tool to meet different ecological objectives.
This project uses computational tools designed to simulate various types of wildland fire spread. The code accounts for multiple parameters including the background wind speed and direction, the burn time of the fuels, the fire-induced weather, and stochastic turbulence effects.
By systematically adjusting each variable, the computational model determines each parameter’s effect on the rate of spread of the fire. Some of the effects on the rate of spread, such as the wind speed, are linear, while other parameters, such as the fuel burn time, result in a nonlinear relationship. These relationships are summarized and can then be related to their real-world applications.
Keywords: wildland fire, fire behavior